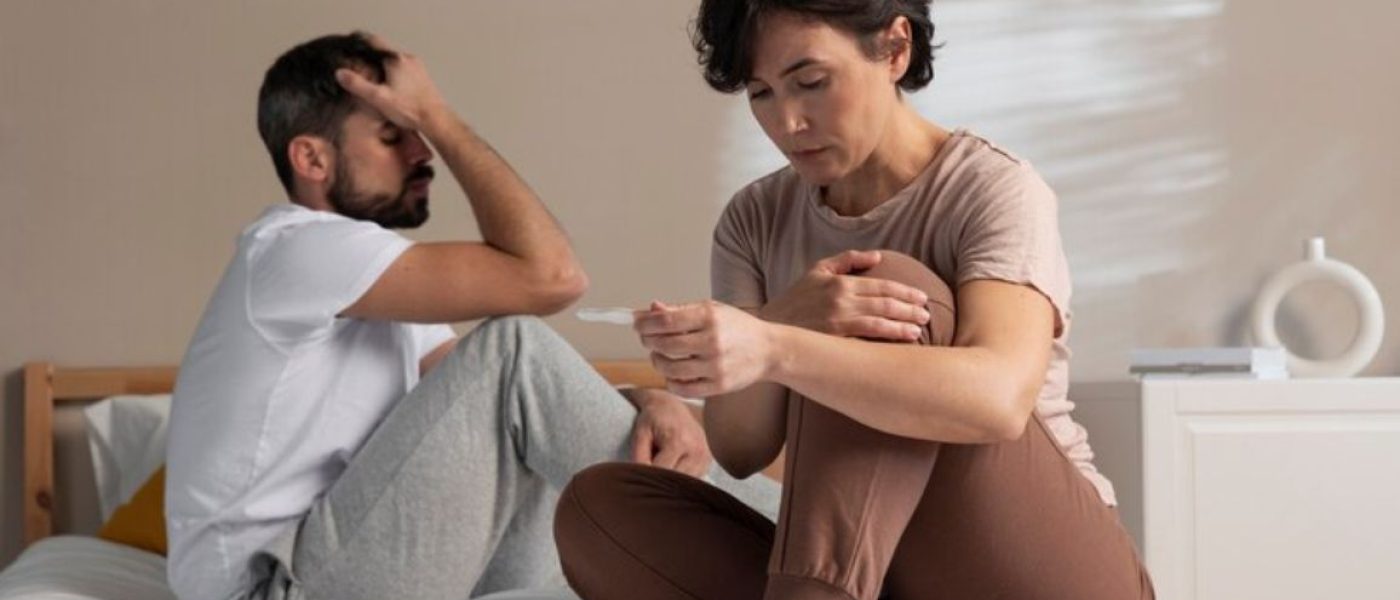

Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections, or rather, conditions, that a person can get from any kind of sexual activity involving one’s mouth, anus, vagina, or penis. Another common name for STIs is sexually transmitted diseases, or even STDs.
There are many kinds of STIs. The most common symptoms are burning, itching, or perhaps discharge in one’s genital area.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), also referred to as sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are, of course, infections that are primarily spread via sexual contact. They can be due to bacteria, viruses, or parasites and can also affect anyone sexually active.
Sexually transmitted infections can indeed lead to sexually transmitted diseases. Treatment can depend on one’s diagnosis.
It is important to note that some STDs can be asymptomatic, meaning they show no symptoms but can still, in fact, be transmitted to others and cause long-term health problems. Regular screening as well as safe sexual practices are crucial for preventing such occurrences and early treatment.
If you are faced with an STD or are experiencing such symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Several STDs are treatable, and early treatment can prevent complications.
Often confused, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are not the same thing.
An infection, which occurs when bacteria, viruses, or parasites attack the body, appears before a disease.
An infection can result in zero symptoms, a disease that usually always comes with clear signs.

An STD usually starts as an STI. However, not all STIs tend to turn into STDs.
If an STD starts with a symptomatic STI, the affected person may initially experience:
Not all STIs have such symptoms.
If an STI progresses to an STD, symptoms can indeed vary. A few of them may be similar to the above, like pain during sexual activity, pain during urination, and irregular or perhaps painful periods.
Other symptoms can be quite different and depend on the type of STD. They can, rather, include:
Sexually transmitted diseases These types are serious and need medical attention.








©2024. Andro9. All Rights Reserved.